
 /
/Going out onto the Internet
Navigating the Internet is like navigating your neighbourhood. A little preparation and awareness makes it much safer.
 /
/The Risks in the Browser
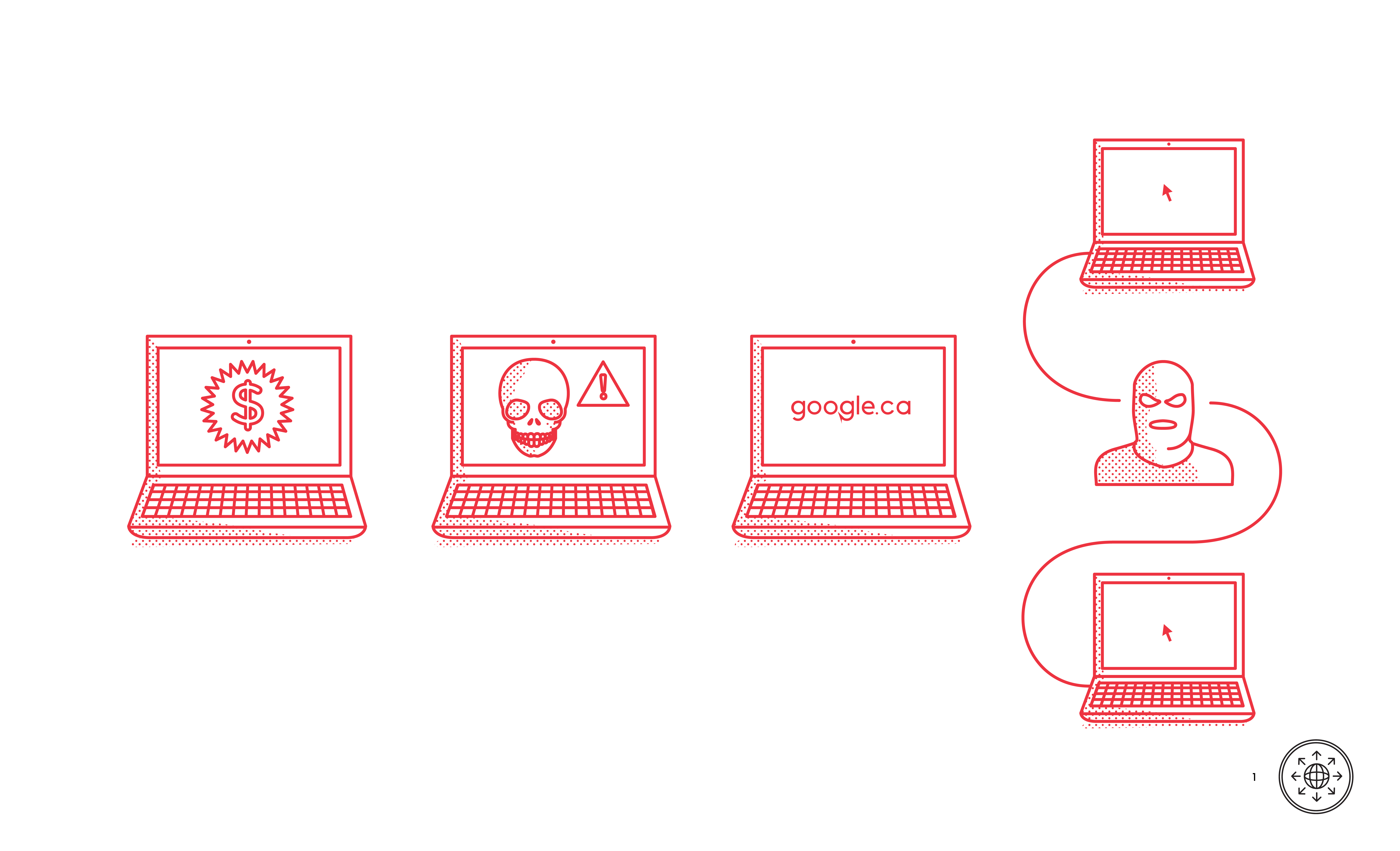
There are many threats on the Internet. Being aware of them can help you to avoid dangers and take action afterwards to minimize harm. Advertising, tracking, drive-by downloads, man-in-the-middle attacks, typo-squatting and phishing are all online dangers.
 /
/What to Look for
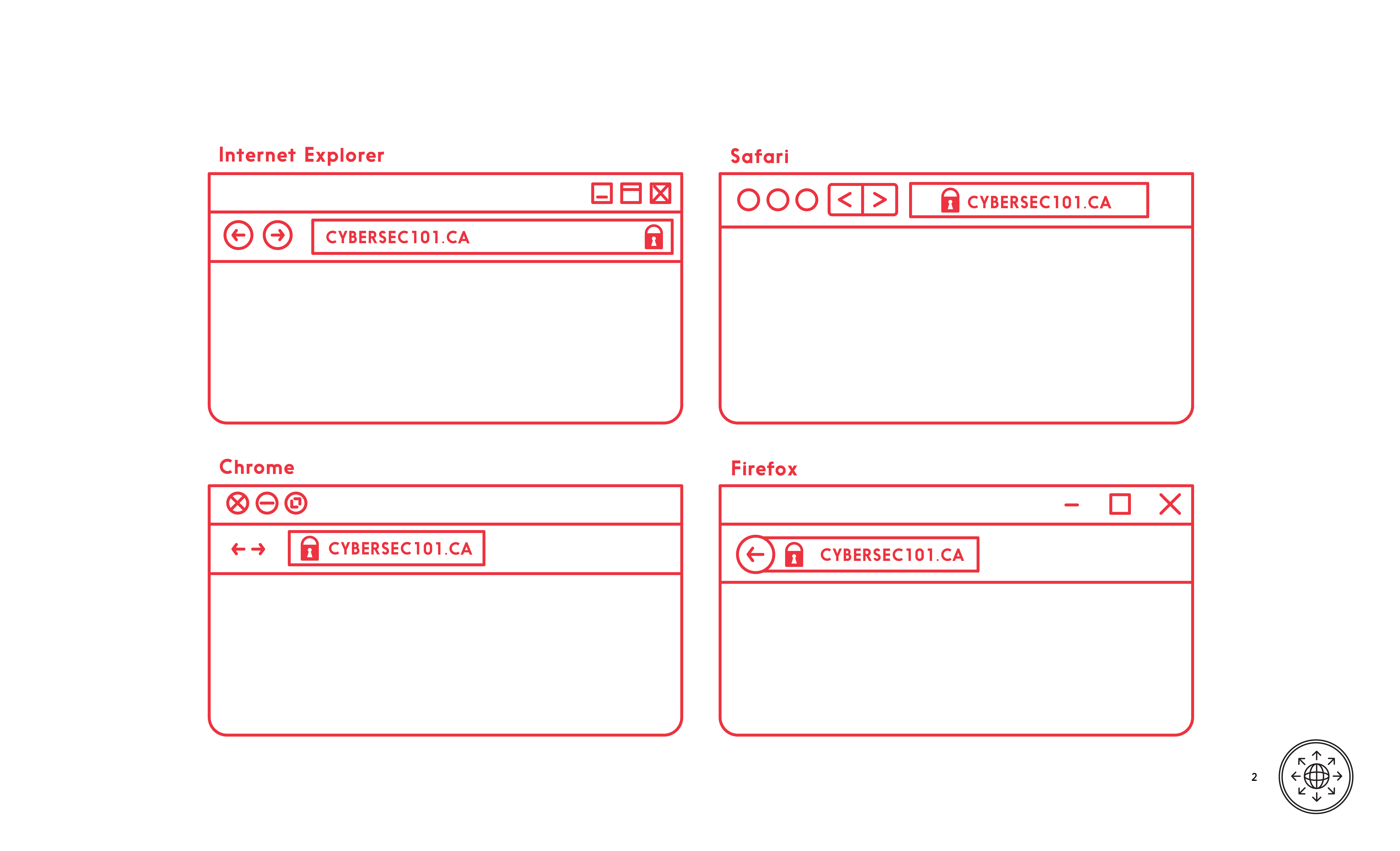
Browsers contain tools to help you navigate the web safely. Use them consciously in combination with critical thinking for a safer web experience. Trust the browser but not the content of the page. Learn about the lock symbol and URL colours for your browser.
 /
/Configuring the Browser
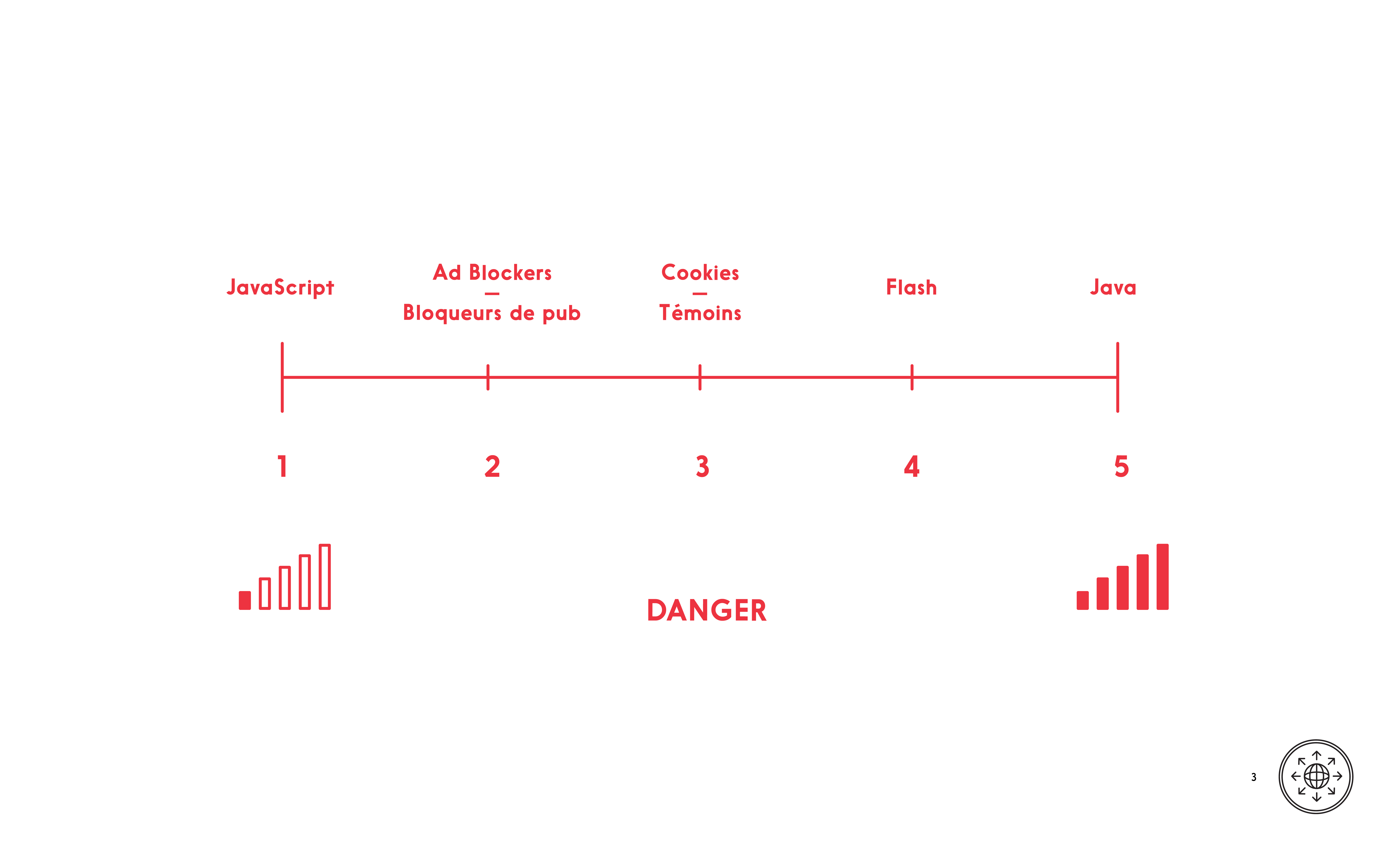
Dangerous websites are written with the same tools as legitimate websites, so it isn’t possible to turn off just the unsafe tools. Disable Java and make an informed choice about Cookies, JavaScript, advertising blocking and Flash.
 /
/Putting it into Practice
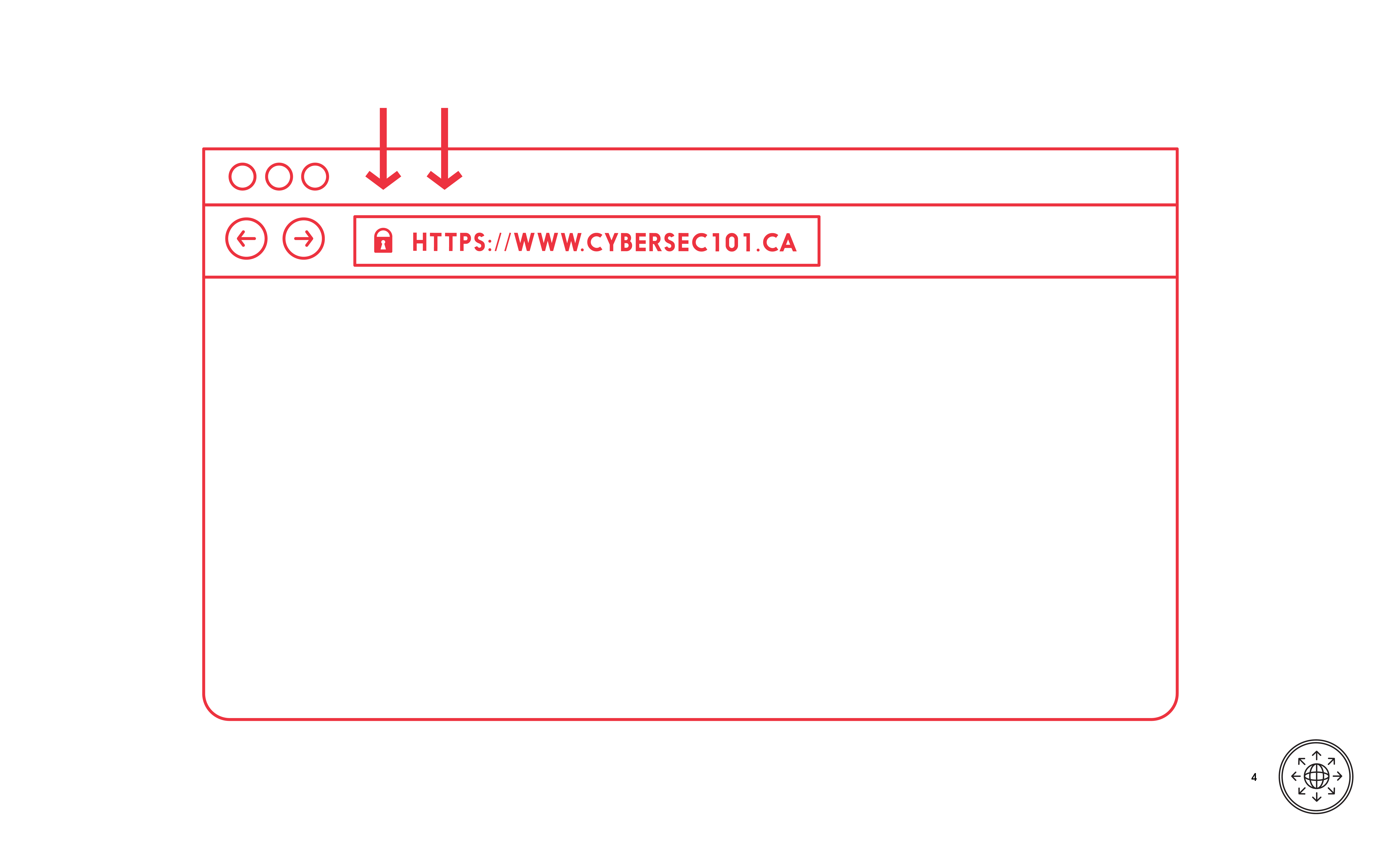
Put what you have learned into practice. Remember to take care with the webpage address, look for security indicators, and warning messages when using an Internet browser.
 /
/Going out onto the Internet
Navigating the Internet is like navigating your neighbourhood. A little prepartation and awareness makes it much safer.
-

Going out onto the Internet
Let’s see how much you have learnt on going out onto the internet.
Test your knowledge and earn your badge to share
START THE QUIZ
- 1/2
Advertising can be a potential security problem because:
It can carry malware
You might buy things you don’t need
Companies can send subliminal messages
It always is spying on you
next question
- 1/2
If you make a mistake when you type a web address incorrectly, it will autocorrect.
True
False
next question
- 1/2
A lock symbol on the page means that the page is safe.
True
False
next question
- 1/2
Security software will solve all of your security worries.
True
False
next question
- 1/2
There are security indicators in a bank webpage so you can tell if the page is counterfeit.
True
False
next question
- 1/2
Security seals in a webpage can be faked.
True
False
next question
- 1/2
If you turn off cookies, or opt out of tracking your privacy is guaranteed.
True
False
next question
- 1/2
Criminals always use bad grammar in phishing pages.
True
False
next question
- 1/2
Privacy mode in the browser provides:
Anonymity for whistle-blowers
Access to your private Internet
Discrete browsing by not keeping a history of browsing on the computer
Absolutely private browsing by hiding all record your activity
next question
-
Going out onto the Internet
your results
/100Congratulations, you earned your badge!
Share on Facebook
Show the answers
Hide the answers
You are on the right track. Some points need to be clarified. Please review the module and try again.
Restart the quiz
1-Advertising can be a potential security problem because:
It can carry malware
You might buy things you don’t need
Companies can send subliminal messages
It always is spying on you
Malvertising is malware distributed by the advertising in webpages.
2-If you make a mistake when you type a web address incorrectly, it will autocorrect.
True
False
Criminals and others will deliberately register web addresses with common typing errors to profit from the mistake with advertising, phishing or malware.
3-A lock symbol on the page means that the page is safe.
True
False
A lock symbol in the browser (outside of the page) can indicate that the connection is encrypted, but does not guarantee whom you are connected to. Be sure the lock icon is in the browser and not in the content of the page.
4-Security software will solve all of your security worries.
True
False
Even with security software you will still need to keep your computer updated and to think critically.
5-There are security indicators in a bank webpage so you can tell if the page is counterfeit.
True
False
Criminals can exactly copy the appearance of any page on the Internet quickly and easily.
6-Security seals in a webpage can be faked.
True
False
Criminals can exactly copy the appearance of any page on the Internet quickly and easily. This includes the security seals. Look for the indicators in the browser.
7-If you turn off cookies, or opt out of tracking your privacy is guaranteed.
True
False
There are many technologies that are used to track people online for advertising purposes. There is no guarantee that your browsing will not be tracked.
8-Criminals always use bad grammar in phishing pages.
True
False
Although it is common to see language mistakes in phishing pages, perfect writing is not a good indicator of safety
9-Privacy mode in the browser provides:
Anonymity for whistle-blowers
Access to your private Internet
Discrete browsing by not keeping a history of browsing on the computer
Absolutely private browsing by hiding all record your activity
Privacy mode will not provide anonymity or absolute privacy but it will reduce the amount of browsing tracking on the computer.
Cheat Sheet
The risks in the browser
Advertising, tracking, drive-by downloads, man-in-the-middle attacks, typo-squatting and phishing all present different types of dangers to be wary of online.
DO be aware of different types of threat so you can spot potential dangers to your information or your system.
What to look for
Browsers contain tools to help you navigate the web safely. Use them consciously in combination with critical thinking for a safer web experience.
DO look closely at the address bar to identify signs of security.
DO be careful to make sure you connect to the correct site.
Configuring the browser
Dangerous websites are written with the same tools as legitimate websites, so it isn’t possible to turn off just the unsafe tools. Learn what these tools are and how to make choices about what to allow in your browser.
DO disable Java and make an informed choice about Cookies, JavaScript, advertising blocking and Flash.
DO use the privacy mode to browse discreetly.
Putting it into practice
Put what you have learned into practice. Remember to take care with the webpage address, look for security indicators, and warning messages when using an Internet browser.
DO take care with the web address, look for security indicators and heed warning messages.
Glossary of Terms
Browser
A browser is a computer program or mobile app that is used to find and look at information on the Internet.
Cache
A cache is where a device can temporarily store some data to speed up future requests.
Certificate
Electronic certificates are used to verify the identity of a webpage.
Cookie
A small piece of information stored on a persons browser for use by a website.
Domain name
The name given to help find a computer on the Internet (e.g. serene-risc.ca).
Drive-by-download
A drive-by-download attack infects your computer with malware just by visiting a page.
Encryption
A process of converting information to a form unreadable to untrusted parties that still contains the original information and is able to be read by the intended recipient.
Extended validation certificate
A certificate that shows that website has gone through some extra validation process to confirm that it is legitimate and indicates the owner of the page.
IP address
An Internet Protocol (IP) address is a set of numbers that a device (computer, printer, etc.) on the Internet uses to identify itself (e.g. 206.167.212.121).
Malvertising
Malicious programs hidden in advertising.
Malware
Software designed primarily for a malicious purpose.
Man-in-the-middle attack
A malicious attack against communications executed between the sender and receiver.
Operating system
An operating system is the main program in a computer such as windows or Apple OSX that makes it possible for other programs to function.
Phishing
Emails, calls or other communication designed to trick you to give away personal information or passwords.
References and Additional Resources
Download SERENE-RISC printable material
Trainers
Trainer Resource – Going out onto the Internet (PDF)
Lesson Plan – Going out onto the Internet (PDF)
Lesson Script – Going out onto the Internet (PDF)
Handout Sheet Answer Key – Going out onto the Internet (PDF)
Resource Sheet – Going out onto the Internet (PDF)
Students
Cheat Sheet – Going out onto the Internet (PDF)
Handout Sheet – Going out onto the Internet (PDF)
Handout Sheet Answer Key – Going out onto the Internet (PDF)
Resource Sheet – Going out onto the Internet (PDF)
Download all the materials for the module “Going out onto the Internet” (PDF)
Additional resources
External Links
Safari Web Settings on iOS
https://support.apple.com/en-ca/HT201265
Deactivating Java in Safari for OS X
https://support.apple.com/en-ca/HT202447
Deactivating Java in Firefox
https://support.mozilla.org/en-US/kb/how-to-turn-off-java-applets
Controlling JavaScript in Windows
https://support.microsoft.com/en-ca/kb/3135465
Managing Cookies in Chrome
https://support.google.com/chrome/answer/95647?hl=en
Managing Cookies in Firefox
https://support.mozilla.org/en-US/kb/enable-and-disable-cookies-website-preferences
Managing Cookies in Internet Explorer
https://support.microsoft.com/en-ca/help/17442/windows-internet-explorer-delete-manage-cookies
Online Behavioural Advertising
https://www.priv.gc.ca/resource/topic-sujet/oba-pcl/index_e.asp
Books
OS X Yosemite: The Missing Manual by David Pogue
2014, O’Reilly Media
ISBN: 978-1-4919-4716-6
Windows 10 All-in-One For Dummies by Woody Leonhard
2015, Wiley
ISBN: 978-1-119-03872-6
Windows 8.1 All-in-One For Dummies by Woody Leonhard
2013, Wiley
ISBN: 978-1-118-82087-2